The Committee on standardisation of protocol for Electric Vehicles (EV) Charging Infrastructure has come out with recommendations entailing specifications for AC and DC charging for electric vehicles. We share information about Electric Vehicle Supply Unit, Home and Public charging, AC & DC charging, Bharath EV specs and other knowledge and insight gained regarding EV charging.
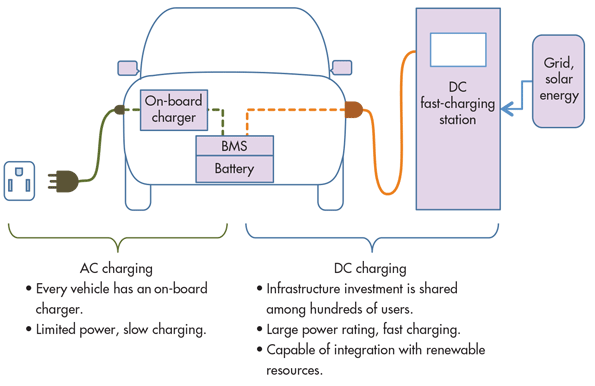
Due to the fact that we have two types of current (AC and DC), there are also two strategies when charging an electric car.
It is possible to use an AC charging station where the on-board charger takes care of the conversion. This option is slower, but cheaper and gentler. AC chargers have an output of up to 22 kWh and the time required for a full charge then depends only on the output of the on-board charger.
It is also possible to use DC stations, where charging is more expensive, but it will take place within a few minutes. Usually their output is 50 kWh, but it is expected to increase in the future. The power of rapid chargers is 150 kWh. Both of them are located around the main arteries and should be used for longer journeys only.